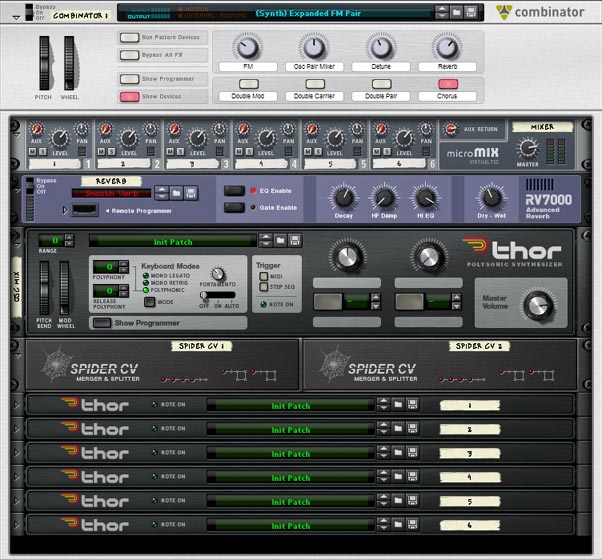
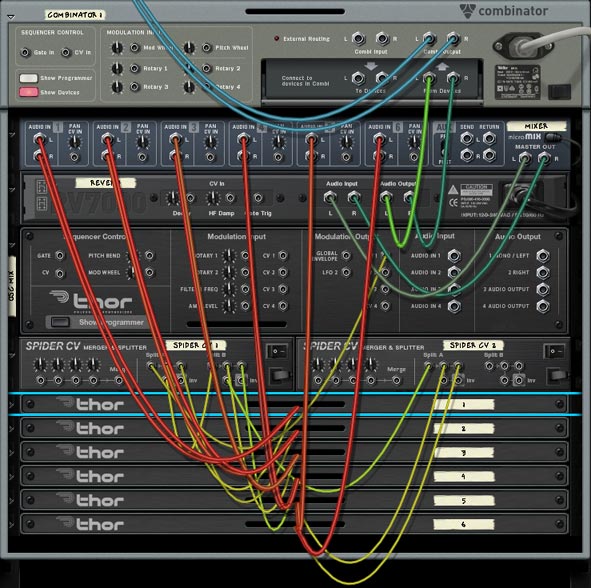
This tutorial should prove a little enlightening for those that only think of Kong as a basic drum module. Here we’re going to twist it into the ultimate controller for everything under the sun. For starters, I’ll show how Kong can control 8 filters at once, and then I’ll move on to use Kong to control the FM Pair Oscillator in Thor. Using some of these methods, you’ll be able to control pretty much anything in Reason or Record with Kong; moving traditional device control from a basic keyboard to a Pad controller.
Sound exciting? I thought so.
You can download the project files here: Taking-Komplete-Kongtrol. This file contains 2 .rns and 2 .cmb files that are outlined below. Both require Reason 5 or Record 1.5 due to the fact that it uses the new Kong device and new CV inputs on the back of the Combinator. There is also a “Volume Control” example .rns file for you to get your feet wet.
Note also that I’ll be unplugged until next Thursday April 15th, so don’t take it personally if I don’t respond to questions until that time. Some times you just have to unplug from things for a bit. But feel free to leave me a little love. I promise to get to all your comments or questions when I jump back online. Have a great week! 🙂
A Little Background
When I was working on my mammoth “Key Flux FX Processor” patch I got a post on the Propellerhead User Forum from someone who jokingly said “what’s next? A Kong controlling Thor? A Thong?” After I stopped laughing and rolling around on the floor, I thought about it for a minute and said “well why not?” And that was the start to this tutorial here. I decided I wanted to try to control Thor with Kong. Whether or not this is practical is for you all to decide. For my part, I can see this being a new fun way to play around with the devices inside Reason.
Understanding the Kong Control Concepts
There are two main concepts that I’d like to outline here. The first is the idea of using the Pads in Kong as an up / down selector switch to transpose MIDI values up or down. The other is the idea of visualizing these changes in Reason, since visualization in Reason (and Kong especially) is somewhat limited.
The first concept was opened up to me by Ed Bauman of EditEd4TV fame. In the midst of his working on recovers for his 80’s band, I asked him to help me figure out how to transpose from one octave to the next using the Kong pads. This helped me set up the Kong Piano Roll Keyboard (again, that was explored in another article). So credit where credit is due. Without his help on that project, I couldn’t have figured out some of these tangential concepts to control other parameters with the Kong pads.
The concept works like this: Using one pad in Kong for the upward movement and one pad for the downward movement, you use the Thor Step Sequencer “Note Transpose” function to manipulate a device parameter that goes from 0 – 127 MIDI value. Each time the up or down pad is pressed, it transposes the value by an increment of “1.” For example, you can go from 64 to 65 to 66 to 67 and so on, using the “Up” pad. Since Reason allows you to interchange CV values (using Note CV for Gate or Gate CV for Note), this isn’t difficult to accomplish.
Here’s the basic setup to control the Volume of a Channel in the Mixer (just as an example):
- Open up Reason with a Main Mixer. Then create a Combinator with a 14:2 Mixer. Underneath that, create a sound generating device (for simplicity’s sake, create a Subtractor and load up your favorite Sub patch). But note that this can be any device you like. Underneath that, create a Matrix and add a pattern in, so that it is playing the Subtractor.
- Now holding the Shift key, create a Kong device. Still holding Shift, create a Thor device and call it “Vol Up.” Completely initialize the Thor device by pulling down all the parameters, removing the Oscillator and Filter, and turning everything to 0 (zero). Also while we’re at it, pull down the level of the Channel on the Mixer where the Subtractor is connected to 0 (zero).
- Open up the Thor programmer, and in the Step Sequencer set the Run Mode to “Step,” Step Count to “1,” and set the first step’s note to “D3.” In the Modulation Bus Routing System (MBRS), set up the following 2 lines in the first 2 slots:
Seq. Note : 100 > S. Transp (Step Sequencer Note : 100 > Step Sequencer Transpose)
Seq. Note : 100 > CV Out1
- Duplicate the “Vol Up” Thor device and rename it “Vol Down.” Then go into this Thor’s Step Sequencer and change the note value of step 1 to “A#2.”
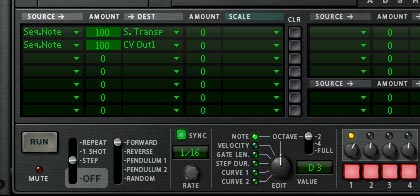
The MBRS / Step Sequencer settings for the "Vol Up" Thor device. - Next, holding the Shift key down, create a Spider CV Merger/Splitter at the bottom of the Combinator rack and name it “Vol Merge.” Now it’s time to route everything up.
- Flip the rack around to the back, and on the Combinator’s 14:2 Mixer, turn the Subtractor channel’s level trim knob up to 127. Then connect the Merged output from the “Vol Merge” Spider to the Level CV input on the Mixer channel.
- Connect the Kong’s pad 1 “Gate Out” CV to the “Gate In (Trig)” CV input on the “Vol Down” Thor. Also connect Kong’s pad 5 “Gate Out” CV to the “Gate In (Trig)” CV input on the “Vol Up” Thor.
- Connect the CV 1 Modulation Output from the “Vol Up” Thor to the “Vol Merge” Spider’s Merge Input 1. Also connect the CV 1 Modulation Output from the “Vol Down” Thor to the “Vol Merge” Spider’s Merge Input 2. Set both trim knobs to a value of “84.” That’s the magic CV number that makes things happen correctly.
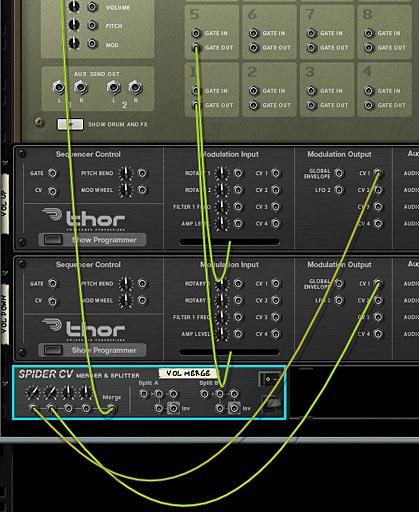
The CV routing for the Up / Down Volume Control using the Kong Pads - Flip the rack to the front again, and label Pad 1 in Kong “Vol Down” and Pad 5 “Vol Up.” Now play your device by pressing “Play” on the Transport and you’ll hear the volume at level 64. Press Pad 5 about 10-15 times and you’ll start hearing the volume rising. Press Pad 1 and the volume drops. You’ve now set up Kong to act as your up / down fader for the volume of your Subtractor device.
Visualizing the Kong Volume Control
Since there’s no visualization in Kong, it’s hard for us to track where the volume is located for the Subtractor. Here’s one way to do it using the DDL-1 device. Note that this trick is curtosy of Sterioevo, and I can’t thank him enough for showing it to me. See the comments to my previous “Kong FX Chain Builder” tutorial for more information on the ins and outs of this visualizing method.
- Building on our previous volume level control, hold Shift down and create a DDL-1 device underneath your Kong device. Label it “Volume Viz” or something like that. Also change the Unit to “MS” for Milliseconds.
- Open up the Combinator programmer, select the “Volume Viz” device, and in the Modulation Routing area, set up the following line:
CV In 1 > Delay Time (MS) : 1 / 127
- This sets up the CV 1 input on the combinator to change the display of the DDL-1 to show values between 1 and 127.
- Now we just need to send the same CV merged signal to also send a value to the CV 1 input on the Combinator, so flip the rack around to the back, and move the CV merged output to one of the A split outputs. Then connect the Merged output to the Split A input on the same “Vol Merge” Spider.
- Finally, send another A split output to the Combinator’s new CV 1 input and turn its trim knob all the way to 127.

You’re all set. Now when you flip to the front of the rack and start pressing the volume pads, you’ll see the value update in the DDL-1 device. I know, it’s pretty sweet. You now have visualization of your volume setting.
A Look at the “Thong 8-Type Filter FX Processor” Combinator
So to answer the question about controlling Thor with the Kong device, I set up 2 patches. The first one is the “Thong 8-Type Filter FX Processor” which can be used as an insert effect on any sound you like. This patch allows you to switch between 8 different filter types and control them all via the Kong pad interface. Here’s a rundown of the pad assignments. Note: You do not want to use any of the Combinator parameters, since all the CV for the Rotaries, as well as the Mod Wheel was used to create the pad assignments and visualization. So simply create a track for the Kong device in the Combinator, and use that track as your control.
Note: I made all the up / down switches bipolar so that everything starts out with a value of 64. This is because each pad press only moves up one midi value, and if you started out at 0 (zero), you’d have a long way to go to get higher up on the register. Starting out at the middle makes working with the up / down pads a lot easier IMHO.
- Pads 5 & 1: Controls the Frequency of all filter at once. Pad 5 moves the filter frequency up and Pad 1 moves the filter frequency down. These two pads together act as the frequency rotary control. Visualization for the Frequency setting can be seen on the “Freq Viz” DDL-1 device located just below the Kong device.
- Pads 6 & 2: Controls the Resonance of all filters at once. Pad 6 moves the resonance up, and Pad 2 moves the resonance down. These two pads together act as the resonance rotary control. Visualization for the Resonance setting can be seen on the “Res Viz” DDL-1 device located just below the Kong device.
- Pads 7 & 3: Controls the Drive of all filters at once. Pad 7 moves the drive up, and Pad 3 moves the drive down. These two pads together act as the drive slider control. Visualization for the Drive setting can be seen on the “Drive Viz” DDL-1 device located just below the Kong device.
- Pads 8 & 4: Controls the LPHP parameter of the “Notch” and “Peak” filters, as well as the Gender parameter of the “Formant” filter. Pad 8 moves the LPHP and Gender parameters up, while Pad 4 moves the LPHP and Gender parameters down. These two pads together act as the LPHP and Gender rotary controls. Note that the filter must be set to “Notch,” “Peak,” or “Formant” for you to hear the effects of these two pads. Visualization for the LPHP/Gdr setting can be seen on the “LPHP/Gdr Viz” DDL-1 device located just below the Kong device.
- Pads 13 & 9: Controls the Envelope Amount of all filters at once. Pad 13 moves the envelope amount up, while Pad 9 moves the envelope amount down. Together, these two pads act as the envelope amount rotary. Note: To turn off the envelope entirely, reduce the envelope amount to 0 (zero) using the “Env Down” Pad (Pad 9). If you wish to insert your own pattern sequence to control the envelopes, change the pattern sequence in the Thor Filter device’s Step Sequencer. Each Thor Filter device Step sequencer controls the corresponding filter envelope, except for the “Peak” Thor Filter, which controls both the “Peak” Thor and “AM” Malstrom filters. Visualization for the Envelope Amount setting can be seen on the “Env Amt Viz” DDL-1 device located just below the Kong device.
- Pad 14: Controls whether the Filter Envelope is turned on or off for all filters. Visualization for this pad can be seen on the fourth band of the “Filter Type Viz” BV512 Vocoder device.
- Pad 12: Controls whether the “Comb” filter is set to plus (+) or minus (-). Visualization for this pad can be seen on the third band of the “Filter Type Viz” BV512 Vocoder device. Note that this is a very specific setting, and the filter type must be set to “Comb” in order for you to hear anything.
- Pad 15: Controls which filter is heard. Visualization for the Filter Type setting can be seen on the first band of the “Filter Type Viz” BV512 Vocoder device. Selections can be one of the following 8 different filter types:
- LP (Thor Low Pass Ladder Filter)
- HP (Thor State Variable Filter – High Pass mode)
- Comb (Thor Comb Filter)
- Formant (Thor Formant Filter)
- BP (Thor State Variable Filter – Band Pass mode)
- Notch (Thor State Variable Filter – Notch mode)
- Peak (Thor State Variable Filter – Peak mode)
- AM (Malstrom AM Filters – both Filter A and B are set exactly the same way when controlling this filter).
- Pad 16: Filter / Bypass. This provides you with a quick way to switch between the Filtered sound and the non-filtered sound. Think of this as a Wet / Dry switch.
A Look at the “Oscillator Kongtrol – FM Pair” Combinator
The second patch is a Kong controlling an Oscillator inside Thor. To start things off easy, I decided to control the FM Pair Oscillator. Again, I made all the up / down switches bipolar so that everything starts out with a value of 64. This is because each pad press only moves up one midi value, and if you started out at 0 (zero), you’d have a long way to go to get higher up on the register. Starting out at the middle makes working with the up / down pads a lot easier IMHO.
The FM Pair Oscillator control has at least one interesting twist. Since controlling the Carrier / Modulator pair is unlike controlling a MIDI value of 0 – 127, we need to figure out the proper settings to control a MIDI value of 1 – 32. This is done by going into the Up / Down Thor devices and changing the note values of the first step to the following:
“Up” Thor device: G#3
“Down” Thor device: E2
Once this is updated, you can control parameters that have 32 options. This does not only mean the FM Pair Carrier and Modulator, but also the Matrix pattern devices, or Thor’s Wavetable Oscillator “Table” selection. Anything with 32 MIDI values can now be controlled and stepped through one at a time in Kong.
Here’s a rundown of the pad assignments. Note: You do not want to use any of the Combinator parameters, since all the CV for the Rotaries, as well as the Mod Wheel was used to create the pad assignments and visualization. So simply create a track for the Kong device in the Combinator, and use that track as your control.
- Pads 5 & 1: Controls the Pitch of the Oscillator. Pad 5 moves the pitch up and Pad 1 moves the pitch down. Visualization for the Pitch setting can be seen on the “Pitch Viz” DDL-1 device located just below the Kong device.
- Pads 6 & 2: Controls the FM Parameter of the Oscillator. Pad 6 moves the fm up and Pad 2 moves the fm down. Visualization for the fm setting can be seen on the “FM Viz” DDL-1 device located just below the Kong device.
- Pads 7 & 3: Controls the Carrier setting of the Oscillator. Pad 6 moves the carrier setting up and Pad 2 moves the carrier setting down. Visualization for the carrier setting can be seen on the “Carrier Viz” DDL-1 device located just below the Kong device.
- Pads 8 & 4: Controls the Modulation setting of the Oscillator. Pad 6 moves the Modulation setting up and Pad 2 moves the modulation setting down. Visualization for the mod setting can be seen on the “Mod Viz” DDL-1 device located just below the Kong device.
- Pads 13 & 9: Controls the Amp Envelope’s “Attack.” Pad 13 moves the Attack setting up (slower attack) and Pad 9 moves the attack down (faster attack). Visualization for the envelope’s attack can be seen on the first and second band of the “Amp Vizualize” BV512 Vocoder device, located just below the 4 DDL-1 devices. The first band shows the upward setting, and the second band shows the downward setting (much easier to see when you are actually using the Kong controller – so download the patch and try it out).
- Pads 14 & 10: Controls the Amp Envelope’s “Decay.” Pad 14 moves the Decay setting up (longer decay) and Pad 10 moves the decay down (shorter decay). Visualization for the envelope’s decay can be seen on the third and fourth bands of the “Amp Vizualize” BV512 Vocoder device, located just below the 4 DDL-1 devices. The third band shows the upward setting, and the fourth band shows the downward setting.
- Pads 15 & 11: Controls the Amp Envelope’s “Release.” Pad 15 moves the Release setting up (longer release) and Pad 11 moves the release down (shorter release). Visualization for the envelope’s release can be seen on the fifth and sixth bands of the “Amp Vizualize” BV512 Vocoder device, located just below the 4 DDL-1 devices. The fifth band shows the upward setting, and the sixth band shows the downward setting.
- Pads 16 & 12: Controls the Panning of the sound. Pad 16 moves the panning left, while Pad 12 moves the panning right. Visualization for the panning can be seen on the seventh and eighth bands of the “Amp Vizualize” BV512 Vocoder device, located just below the 4 DDL-1 devices. The seventh band shows the leftward setting, and the eighth band shows the rightward setting.
Where can you go from Here?
Sometimes it’s the smallest concepts that can lead to the biggest revelations; opening doors to new ideas and solutions. This is definitely one of those cases. Using these simple ideas, you can now control virtually every possible parameter in Reason via the Kong Pads. These are just two types of control devices I built here. But there’s nothing stopping you from building a Reverb Kong controller (ReKong 7001?), or a DDL-1 controlled by Kong (DDKong-2?). And there’s nothing stopping you from building a controller that allows you to combine Oscillators or Filters or any number of things together that can be triggered by Kong pads. Just use your imagination and come up with some cool ways to take your pad controlling to new heights. This is just the tip of the iceberg. Where you go from here is all up to your patience and ambition.
Any thoughts?