In this tutorial I’m not going to outline any grandiose Combinator or showcase some majorly complex CV routing scheme (though I have a few interesting ones that I may show down the road). Instead, I’m going to outline just some of my favorite quick tips that you can use when you find yourself in a bit of a bind with Reason. Hopefully these little tips open you up to a new way of thinking with the software, or else at least point you into a direction in case you get stumped.
All of the tips below came out of a need I had to get out of jail with the software. In other words, I’d find myself at a standstill unable to go further because I’d locked myself in a hole. Here’s a few ways I found to get out and escape. I hope you find these tidbits useful.
Tip #1: Unison = Stereo (It’s not just big fat sound).
The first tip came out of a post I’d seen on the PUF (Propellerhead User Forum) entitled “Confessions.” In this post, a few people had stated that they never used the Unison device, and didn’t really understand what it was for. “I think it has something to do with fattening up the sound, but I don’t really use it and don’t really know what it’s for.” Fair enough. Here’s what I think:
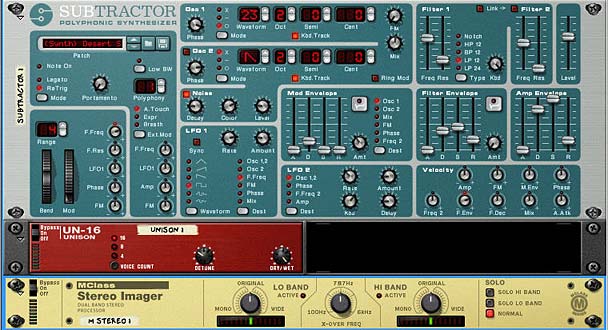
Yes, it fattens up the sound. But it does more than that. For instance, take any monophonic sound device; The Subtractor and Thor come to mind. If you start playing either device, you can tell it sounds monophonic. In the case of Thor, you can do some clever things like add some Chorus and Delay. Perhaps in the Subtractor, you’ll add some ring modulation or FM synthesis, detune two oscillators together. But here’s the dilemma: you add a Stereo Imager after the device and nothing happens? Why?
This is because the Stereo Imager only works on Stereo audio, and since you have a device which is monophonic, nothing is going to happen. The simple fix: add a Unison device between the sound source and the Stereo Imager. Instantly, you’ve turned your sound into a Stereo audio pair going into the Stereo Imager, which can now effect the sound as you want (point of fact, it’s more of a faux stereo, but it works).
The unison device is there to “Stereo-ize” your monophonic sound. At the same time, it fattens the sound by creating multiple detuned voices out of the audio you send into it. Good enough!

Tip #2: Mixer Pan/Level CV automation is holding me back!
Ever automate the level and/or Pan info on your main mixer in Reason or Record and then realize you can’t alter it at all. For instance, if you send a Subtractor LFO to fully automate the level of your track, you end up unable to alter or change the level to fade it in or out right? Whatever is playing in a clip in your sequencer will be affected by the LFO as is. No fade ins, no fade outs, no changes along the way. Same goes for panning.
Here’s a simple tip to allow you to have both. And again it involves inserting a device between the sound source and the mixer. In this case, it’s another line mixer. Insert a 6:2 mixer between your main mixer and the sound source. Then flip the rack around and move the audio cables from the sound source into Channel 1 on the 6:2 line mixer. Then send some audio cables from the main output on the line mixer into the previous channel on the main mixer. Now you can flip back to the front again and right-click on the Channel 1 level knob, select “Edit Automation” and enter your fade-ins and fade-outs. You can also adjust your panning on this line mixer as well. This will affect the panning of the sound source before it gets sent into the main mixer where the CV is affecting the panning. In this case, the panning is combined together.

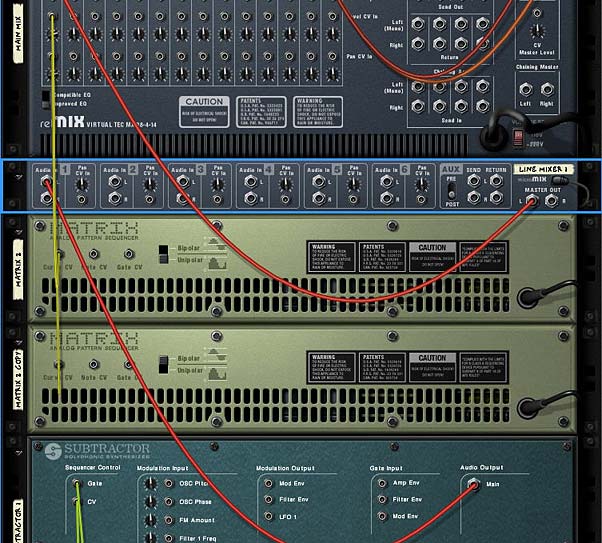
There you go. Total control over your mix, even when your mix is being controlled by CV.
Tip #3: While we’re on CV, don’t forget you can automate any CV trim knob on the back of any device
I discussed this tip in full here: #7 – Adjustable CV, but it bears repeating. If you want to control the trim pots for any CV connection (you know, the tiny knobs on the back of your devices into which you send the CV cables), simply insert a Thor device between the CV source and the CV destination. Route the CV into the CV in 1 within Thor, and send it out from CV out 1. Then in the modualtion Bus Routing Section of Thor (MBRS), use CVin1 as a source and CVout1 as a destination. Enter 100 as an Amount, and then use Thor’s Rotary 1 as a Scale (also with an amount of 100). Put everything (source/destination devices as well as the Thor “CV Pass-Through” device) into a Combinator, and program the Combinator’s Rotary 1 to adjust Thor’s Rotary 1.
This means that you’re adjusting the Scale amount value using the Combinator Rotary 1. Essentially, this will have the same effect of adjusting your CV trim pot. Sounds complicated, but it’s really quite simple.
Tip #4: Damn it, there’s no CV connection. But I want to automate it with an LFO!
Enter the Combinator to the rescue. For this trick to work, you have a device which has a parameter you want to affect with an LFO (or any other mod envelope or anything you like) and the device with the LFO which is going to affect it. This couldn’t be easier, but it’s not at first obvious. Here’s what you do:
Put both devices in a Combinator. Flip the rack around. Send the CV from the LFO device into the Rotary 1 CV in of the Combinator. Then flip back around to the front, and open up the Combinator programmer. Select the sound device. In the Modulation Matrix, use Rotary 1 as the Source andthe parameter you want affected in the destination device as the “Destination.”
Now, when the LFO is enabled and running, it gets sent along the CV cable and affects Rotary 1 on the Combinator. Rotary 1 on the Combinator in turn is affecting the parameter on your destination device. In other words, the Combinator Rotary 1 is used as a CV pass-through to affect any parameter you like, not just the ones that have CV slots on the back of the devices.
Tip #5: That nasty bypass click.
Not all glitch sounds are good sounds. Such is life when you are dealing with bypass switches in Reason. Sometimes you’ll get this nasty clicking sound when switching from on to bypass or vice versa. Sometimes you’re lucky and you don’t get it. It’s like Russian Roulette audio-style. This is why I never ever use the bypass switch. And also why I never ever automate it. Instead, here’s a few simple ways to get the same benefit without the horrible clicks.
First off, if you’re using a device that has a dry/wet knob, put it in a combinator and tie the dry wet knob to a button or a rotary. There’s your bypass button.
If, on the other hand, you need to get around bypassing an entire Combinator, try this trick. Inside the combinator create a spider and a second line mixer (assuming you already have a line mixer for the main audio). Then split the audio coming into the combinator, and have one split going to the main line mixer and the other going to the second line mixer. Merge the master outputs of both line mixers in the merge section of the spider, and then back out to the Combinator “From Devices” output. Ensure all your FX and Instrument devices go into channels on the main mixer. Leave the second mixer for the dry signal only, and nothing else.
In the Combinator programmer, program a button to switch between the two mixers. So when the button is off, the master level on the main mixer is at 0, while the master level on the secondary mixer is at 100. When the button is on (lit), the master level on the main mixer is at 100, while the master level on the secondary mixer is at 0. The button now acts as a bypass. When off, the signal is bypassed and the audio goes right through the Combinator unaffected. When the button is on, the Contents of the Combinator are enabled and the sound affected can be heard. Instant bypass without any clicking issues.
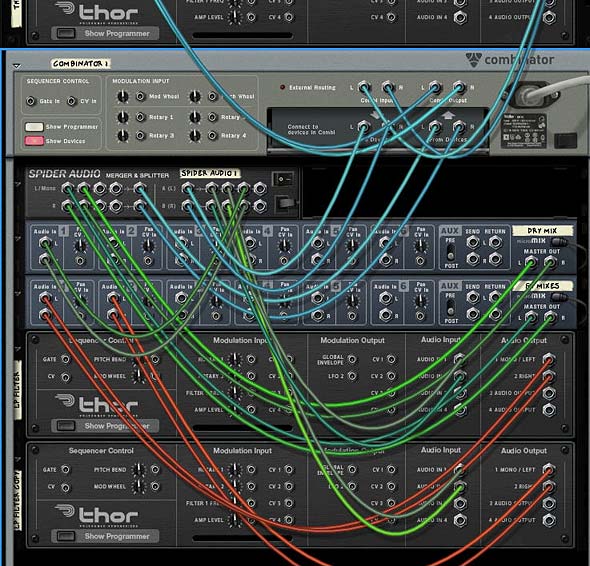
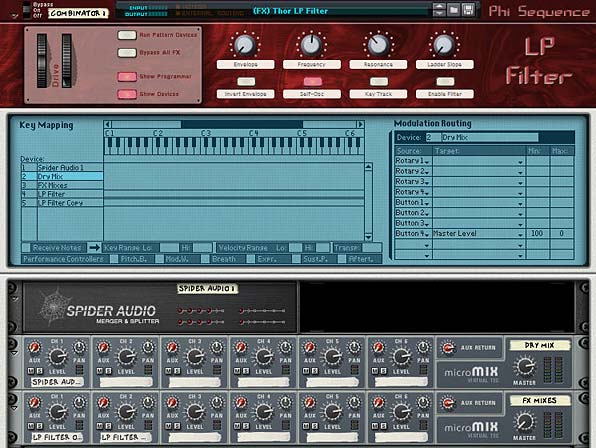
Keep in mind there are some things that just can’t be stopped on a dime. For instance, changing the delay time or automating changes to the delay time will result in a very distinct sound, almost like a pitch shifting. You just can’t get around this. That’s the nature of audio. So while bypassing most things works without any side effects, other things can still be noticeable. The idea, however, is to minimize the unwanted audio problems as much as you can.
I hope you found these tips useful. I’ll keep posting more as time permits. In the meantime, feel free to share your thoughts or your own tips here by posting a comment. Happy Reasoning!